1. Introduction
Electronic components are the building blocks of modern technology, forming the basis of all electronic circuits. From simple devices like flashlights to advanced systems like smartphones and computers, these components play a crucial role in managing electrical signals and enabling functionality.
Understanding the types of electronics components is essential for anyone exploring electronics, whether you’re a hobbyist, a student, or a professional. A basic knowledge of these components helps in designing circuits, prototyping projects, and understanding how electronic devices function.
In this article, we’ll provide a clear overview of the types of electronics components, focusing on their classification and roles in circuits. This guide is designed to give beginners a foundational understanding of these essential elements.
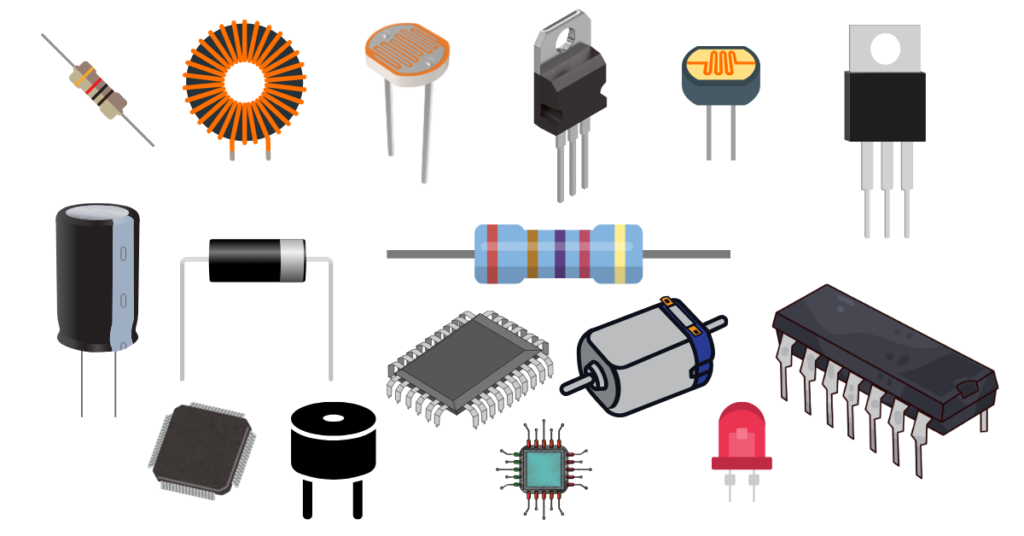
2. Classification of Electronics Components
Electronic components can be broadly classified into three main categories: active components, passive components, and electromechanical components. Each category plays a unique role in circuits, enabling a wide range of electronic functions. Understanding these classifications is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electronic systems.
2.1 Active components
Active components require an external power source to operate and are capable of controlling or amplifying electrical signals. They are essential for complex circuit operations and signal processing.
Examples:
Transistors: Widely used for switching and amplifying signals.
Integrated Circuits (ICs): Compact components capable of performing multiple tasks like computation and signal processing.
Diodes: In most cases, diodes are considered active components because they control the flow of current in one direction and often require a voltage (forward bias) to operate.
2.2 Passive Components
Passive components do not require an external power source and cannot amplify signals. They only store, dissipate, or transfer energy in a circuit.
Examples:
Resistors: Reduce current flow or divide voltage in circuits.
Capacitors: Temporarily store electrical energy and filter signals.
Inductors: Store energy in a magnetic field.
Note: Diodes can sometimes act as passive components, such as in rectification (converting AC to DC) where they control current without amplifying or adding external energy.
2.3 Electromechanical Components
Electromechanical components combine electrical and mechanical functionality to perform tasks like switching, movement, or generating sound. These components are essential in systems that require physical control.
Examples:
Switches: Manually or automatically control the flow of current.
Relays: Electrically operated switches used for isolating circuits.
Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical motion.
3. Conclusion
Electronic components are the building blocks of modern devices, from simple gadgets to complex systems. This article provided a brief overview of the types of electronics components, including active, passive, and electromechanical components, and their basic roles in circuits.
To learn more about electronics and embedded systems, visit Maitronics for detailed guides, tutorials, and resources.
For any inquiries or feedback, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected].
Follow us on social media for updates, tutorials, and insights!
